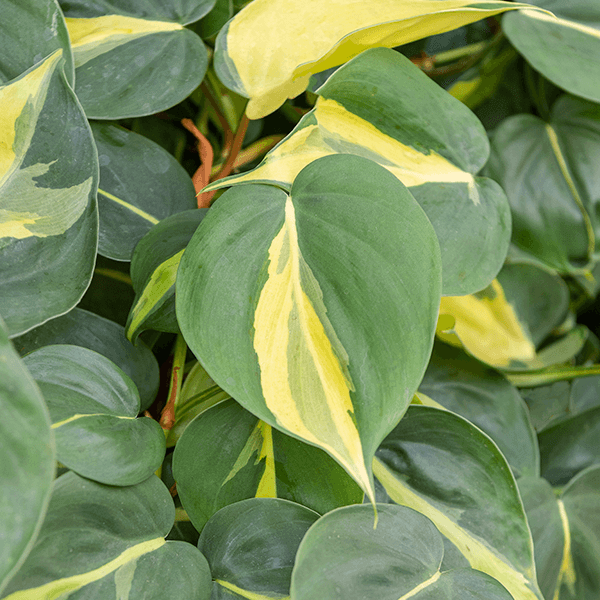
how to care for philodendron scandens

quick care guide philodendron scandens
 |
Once a week in summer; once every 2 weeks in winter |
 |
Does well in low to medium sun |
 |
Fertilize once every two weeks in the summer |
 |
Toxic to pets |
 |
Strong air purifier |
Provide bright, indirect sunlight, grow in well-draining soil and keep the soil slightly moist. Reduce watering during the fall and winter, fertilize lightly every month, and pinch back the stems to create a fuller, bushy plant.
detailed care guide for philodendron scandens
Scientific Name: Philodendron Scandens (a.k.a. Philodendron Hederaceum, Heartleaf philodendron)Varieties: (list only includes varieties sold by Leafy Life)
- Philodendran Scandens – the original Scandens with dark green leaves
- Philodendron Scandens ‘Brasil’ – yellow variegation that can vary in intensity from leaf to leaf
Origin: Rainforests of tropical Central and South America
Light: Philodendrons can be acclimated to nearly direct sunlight in the right conditions, but they thrive in light shade. If you notice many of the leaves turning yellow at the same time, it can indicate you are giving the plant too much direct light. If you notice it is getting leggy, it may need more light.
Water: Keep the growing medium moist at all times. Push aerial roots into the soil on climbing varieties. Keeping the plants moist during winter when indoor air can get very dry can be a challenge. At the same time, avoid overwatering or root rot may develop. If the leaves are drooping, it can indicate either too much water or not enough – you can tell by checking the soil.
Soil: Philodendrons like rich, loose potting soil that will drain well but is still high in organic matter. They can grow in 100% sphagnum peat moss.
Temperature: Their temperature range is variable, but no Philodendron likes going below about 13°C for long.
Fertilizer: Philodendrons will produce larger leaves and remain healthier if you fertilize them regularly. Use slow-release pellets at the beginning of the growing season, or bi-weekly liquid fertilizer.
Humidity: They like humidity, so you might maintain the humidity around them with a pebble tray of water. Mist them frequently during the growing season, about every two days. During the winter you should mist them every three to four days.
Pruning: Pinch back the stems of your heartleaf to keep them from getting too leggy or stringy. This triggers growth from growing points at the nodes on the stem, creating a fuller, bushier plant. You can pinch the stems back at any time but it’s best to do it when the plant is actively growing during the warmer months. When you pinch them, make sure to create a clean cut directly after a leaf node using either your fingernails or a sharp pair of clean scissors.
Re-Potting: Your Heartleaf Philodendron should be repotted every 2-3 years to provide it with fresh potting soil and ensure the container is big enough for the root system. A plant that is root-bound in a container will have slower growth.
Propagation: Climbing Philodendrons are easy to propagate from stem cuttings placed in a glass of water. Rooting hormone will increase the chances of success but is usually not necessary. Once a good network of roots has become established in water, pot up the new specimen.
Diseases and Pests: Diseases and pest problems in Philodendrons are not common, although they do exist. One of the biggest culprits of both is overwatering so watering plants only when they need it will help prevent problems.
Toxicity: These plants are poisonous. Keep them away from children and pets and take care when handling.
philodendron scandens origins & overview
There are over 400 different species of philodendrons, covering a variety of growing methods, leaf shapes, etc. For simplicity’s sake, these different species can be classified as either climbers or non-climbers. Climbers are well suited for homes and indoor office spaces because plants are smaller in stature. Non-climbers are capable of growing into immense plants with large, deeply-lobed leaves; they are more suited for public spaces and are often found in shopping malls, museums, and similar settings. Of the climbing philodendrons, the most common and one of the easiest known houseplants to grow is the heartleaf philodendron, or Philodendron Scandens. Originating from the rainforests of South America it is also known as the sweetheart philodendron.philodendron scandens light requirements
Heartleaf Philodendrons are popular in homes because they have low light requirements compared to many other types of houseplants. They originate from the rainforest floors of South America, where there is little direct light beneath the forest canopy. Place your Philodendron where it can receive bright, indirect light for a minimum of three to four hours a day. Plants will also tolerate a range of lighting conditions from diffused light to almost full shade, and even thrive when grown indoors under fluorescent lights. Avoid putting your plants where they can receive direct sunlight as this can burn the leaves. Just note that the lower the light conditions, the slower the plant growth. Small leaves or long spaces between leaves show that the plant is not getting enough light.
how to water the philodendron scandens
During the active growing season in the spring and summer keep the potting soil slightly moist, although not soggy, at all times. During the winter when growth is slower, allow the top part of potting soil to dry out completely before watering. Yellow leaves indicate over-watering and brown leaves mean the plant needs more water.repotting the philodendron scandens
Some of the philodendron varieties are extremely fast-growers, especially the climbers. Pinch off the new growth to keep the plant manageable and repot them annually as they outgrow their pots.

Decorative pots are approx. 11 cm.

Plants have a diameter of 11 to 13 cm.
Decorative pots are approx. 14 cm.

Plants have a diameter of 14 to 16 cm.
Decorative pots are approx. 17 cm.

Plants have a diameter of 17 to 19 cm.
Decorative pots are approx. 20 cm.

Plants have a diameter of 20 to 24 cm.
Decorative pots are approx. 25 cm.
extra small |
Plants - 8 to 10 cm diameter Pots - 11 cm |
small |
Plants - 11 to 13 cm diameter Pots - 14 cm |
medium |
Plants - 14 to 16 cm diameter Pots - 17 cm |
large |
Plants - 17 to 19 cm diameter Pots - 20 cm |
extra large |
Plants - 20 to 24 cm diameter Pots - 25 cm |